European Space Agency Earth observation.

Earth Observation satellites.
How satellites collect data and make the information available.
There are a huge number of satellites circling the Earth collecting data and understanding what they do and how they work is not always well explained. The intention here is to explain how a number of missions collect and share data to give an accurate story of the working of the planet.
The European Space agency has a comprehensive plan and it is interesting because it pulls to gather the collective science from 28 nations with 24 languages and 500 million people. It is interesting to see these countries pull together to make a comprehensive plan to monitor the Earth’s climate and share the information amongst hundreds of universities and government agencies and thousands of scientists around the world. The information is free to the world and is used by many small countries to manage disasters and their environment.
This is a very shortened and simplified version of how it works.
The information and pictures are taken from the European Space agency web site.
How satellites collect data and make the information available.
There are a huge number of satellites circling the Earth collecting data and understanding what they do and how they work is not always well explained. The intention here is to explain how a number of missions collect and share data to give an accurate story of the working of the planet.
The European Space agency has a comprehensive plan and it is interesting because it pulls to gather the collective science from 28 nations with 24 languages and 500 million people. It is interesting to see these countries pull together to make a comprehensive plan to monitor the Earth’s climate and share the information amongst hundreds of universities and government agencies and thousands of scientists around the world. The information is free to the world and is used by many small countries to manage disasters and their environment.
This is a very shortened and simplified version of how it works.
The information and pictures are taken from the European Space agency web site.

There are three major groups of Earth Observing programs and these are the Sentinel program which covers marine, land, atmosphere, emergency, security and climate, MeteoSat for weather and the Dynamic Earth program. These will be explained later.
Each satellite might carry four or five instruments to collect data on an orbit and these can be grouped into two types which are, either passive or re-active. The passive instruments receive data like a camera or the eye and the re-active instruments send a signal like radar and catch the rebounding signal to record the information. The data for both types is collected in the form of digitised radio waves.
In addition most satellites have an altimeter and a GPS to give height and position of the satellite and there are also ground based stations that will fire a laser signal to verify height and position.
Each satellite might carry four or five instruments to collect data on an orbit and these can be grouped into two types which are, either passive or re-active. The passive instruments receive data like a camera or the eye and the re-active instruments send a signal like radar and catch the rebounding signal to record the information. The data for both types is collected in the form of digitised radio waves.
In addition most satellites have an altimeter and a GPS to give height and position of the satellite and there are also ground based stations that will fire a laser signal to verify height and position.
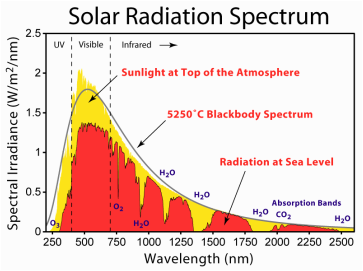
A brief explanation of radio frequencies.
To explain how radio frequencies can be tuned to collect data, this illustration is of radiated wavelengths, from the 5750 C temperature of the Sun down to the 14 C radiated temperature of the Earth.
To explain how radio frequencies can be tuned to collect data, this illustration is of radiated wavelengths, from the 5750 C temperature of the Sun down to the 14 C radiated temperature of the Earth.
From the overall wide range of frequencies available for observation they can be divided down further into frequencies suitable for observing different subjects. The shorter the wavelength the greater the detail.
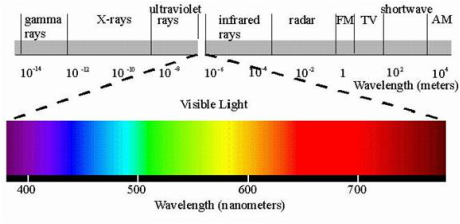
If we then concentrate on just the light spectrum we get frequencies that are these.
This illustration is only for visible light whereas satellite instruments can be tuned to a very much wider range of frequencies depending on what needs to be observed..
This illustration is only for visible light whereas satellite instruments can be tuned to a very much wider range of frequencies depending on what needs to be observed..

Passive receiver instruments.
Passive instruments receive and collect a signal in the same way that a camera or your eye does but because it is digital it can receive a much wider range of frequencies than just the spectrum of light. On either side of the light frequencies are ultra violate and infra-red. The infra-red frequencies are useful because they are not blocked by water vapour or CO2 and can get a clear signal during night or day.
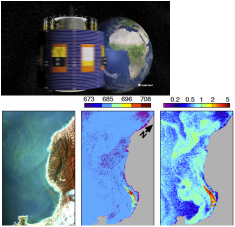
So if we have a targeted receiver that looks at a very small area of the land and tune it to the green spectrum at 540 nm we can measure the health of plants, and if it was examining a section of forest, we can determine how healthy the forest is and how much CO2 it is absorbing. As autumn approaches and the leaves change colour the value of the signal will alter and this can be analysed to see how much CO2 the forest is releasing .
Passive instruments receive and collect a signal in the same way that a camera or your eye does but because it is digital it can receive a much wider range of frequencies than just the spectrum of light. On either side of the light frequencies are ultra violate and infra-red. The infra-red frequencies are useful because they are not blocked by water vapour or CO2 and can get a clear signal during night or day.
So if we have a targeted receiver that looks at a very small area of the land and tune it to the green spectrum at 540 nm we can measure the health of plants, and if it was examining a section of forest, we can determine how healthy the forest is and how much CO2 it is absorbing. As autumn approaches and the leaves change colour the value of the signal will alter and this can be analysed to see how much CO2 the forest is releasing .
The same system of measurements can be made with the colour of the oceans to measure plankton, salinity or with a different, but still passive, frequency to measure the temperature.
The amount of information that can be gathered in this way is huge and the resolution of surface area readings is getting finer and finer so that we can now get down to about 20 metres to measure individual trees and the state of crops in a field. This of course produces a fantastic amount of information that has to be received, stored and analysed.
The amount of information that can be gathered in this way is huge and the resolution of surface area readings is getting finer and finer so that we can now get down to about 20 metres to measure individual trees and the state of crops in a field. This of course produces a fantastic amount of information that has to be received, stored and analysed.
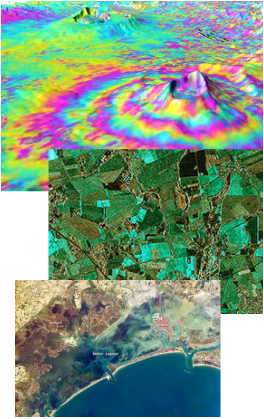
Re-active instruments.
Re-active instruments send a directed radio signal and measure the return signal just like radar and the quality of instruments today measurements can be down to millimetres. Some of the instruments scan with laser to get very fine readings. In this way a very accurate profile of the Earth can be gained. Productivity of crops can be monitored with accuracy down to individual sections of a field. The height of trees in a forest can be measured and combined with the colour readings to give the mass of growth and health of a forest and determine the amount of CO2 absorbed or produced.
With accurate measurements pack ice can be measured, both with the height of the ice pack which then gives ice thickness, and the area of an ice flow and from that the total volume of the ice.
If the readings from the temperature instruments are then overlaid on the same plot, the information can be corroborated as water has a different temperature to ice and more information gained.
Re-active instruments send a directed radio signal and measure the return signal just like radar and the quality of instruments today measurements can be down to millimetres. Some of the instruments scan with laser to get very fine readings. In this way a very accurate profile of the Earth can be gained. Productivity of crops can be monitored with accuracy down to individual sections of a field. The height of trees in a forest can be measured and combined with the colour readings to give the mass of growth and health of a forest and determine the amount of CO2 absorbed or produced.
With accurate measurements pack ice can be measured, both with the height of the ice pack which then gives ice thickness, and the area of an ice flow and from that the total volume of the ice.
If the readings from the temperature instruments are then overlaid on the same plot, the information can be corroborated as water has a different temperature to ice and more information gained.
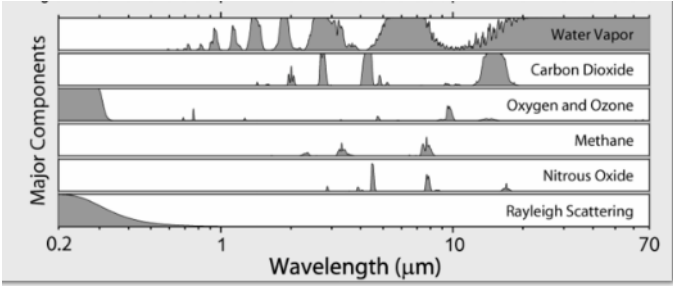
Gasses.
A very similar thing can be done with greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere in that they allow a signal to pass though at one frequency and yet block a signal at another frequency. Choosing the frequency of signal to suit the different gasses gives an accurate reading. This information can be overlaid on the forest plots and the CO2 consumption or output of the forest can be measured.
A very similar thing can be done with greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere in that they allow a signal to pass though at one frequency and yet block a signal at another frequency. Choosing the frequency of signal to suit the different gasses gives an accurate reading. This information can be overlaid on the forest plots and the CO2 consumption or output of the forest can be measured.
Sentinal programs Living planet.
These are the work horses of the ESA program,
The first satellites in this highly sophisticated program were Envisat, RadarSat and ERS which were highly successful when launched in 1992 and they operated for ten years. They have been replaced by 5 Sentinal satellites which each carry four to eight instruments and are the workhorses of earth observation. They measure and record every part of the Earth's environment including farming efficiency, moisture content, fires, civil emergencies such as floods and oil spills, oceans observation for plankton,temperatures, sea height, atmospheric gasses and can help any country around the world with ways of managing their country.
These are the work horses of the ESA program,
The first satellites in this highly sophisticated program were Envisat, RadarSat and ERS which were highly successful when launched in 1992 and they operated for ten years. They have been replaced by 5 Sentinal satellites which each carry four to eight instruments and are the workhorses of earth observation. They measure and record every part of the Earth's environment including farming efficiency, moisture content, fires, civil emergencies such as floods and oil spills, oceans observation for plankton,temperatures, sea height, atmospheric gasses and can help any country around the world with ways of managing their country.
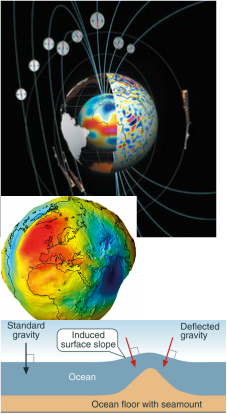
Earth Explorers.
There are three satellites so far in the Earth Explorer program, GOCE (replaced by Cluster), SMOS and CryoSat and more in planning stage.
GOCE and CLUSTER are gravity measuring satellites that have mapped the Earth with extreme accuracy. When an altimeter satellite measures the surface of the sea there are high spots where the gravitational pull of an underwater sea mount will make the sea level a bit higher. Once this is known it can be deducted from the altimeter reading and a more accurate, smoothed set of reading is obtained. GOCE was very successful but has now been replaced with a mission called Cluster which is an array of three satellites that does much more than GOCE because it also measures the magnetic and gravitational fields around the world and down into the centre of the Earth. It can also indicate geothermal resources under the crust, aquifer and oil well depletion, glacier melt and a great deal more.
There are three satellites so far in the Earth Explorer program, GOCE (replaced by Cluster), SMOS and CryoSat and more in planning stage.
GOCE and CLUSTER are gravity measuring satellites that have mapped the Earth with extreme accuracy. When an altimeter satellite measures the surface of the sea there are high spots where the gravitational pull of an underwater sea mount will make the sea level a bit higher. Once this is known it can be deducted from the altimeter reading and a more accurate, smoothed set of reading is obtained. GOCE was very successful but has now been replaced with a mission called Cluster which is an array of three satellites that does much more than GOCE because it also measures the magnetic and gravitational fields around the world and down into the centre of the Earth. It can also indicate geothermal resources under the crust, aquifer and oil well depletion, glacier melt and a great deal more.

CryoSat is a Polar orbiting satellite that has very sensitive radar altitude instruments that can measure ice height to within millimetres. This means that it can scan an ice flow to measure the ice packs height and the open water around it and from this can gauge the extent of the ice and the total mass of floating ice. CryoSat is also proving useful for profiling the land and lakes.
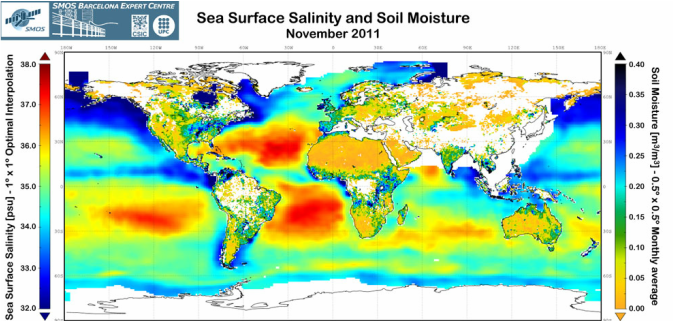
ESA's Soil Moisture Ocean Salinity (SMOS) Earth Explorer mission is a radio telescope in orbit, but pointing back to Earth not space. It's Microwave Imaging Radiometer using Aperture Synthesis (MIRAS) radiometer picks up faint microwave emissions from Earth's surface to map levels of land soil moisture and ocean salinity
There are other missions such planned such as ADM-Aeolus, Earth CARE and Biomass.
There are other missions such planned such as ADM-Aeolus, Earth CARE and Biomass.
Weather satellites.
MeteoSat satellites are geostationary over Europe and there are always two working in case one fails prematurely. They spin while in position and scan the Earth so that the area of cover is scanned every 15 minutes. They report on weather and emergencies such as oil spills and floods.
MeteoSat satellites are geostationary over Europe and there are always two working in case one fails prematurely. They spin while in position and scan the Earth so that the area of cover is scanned every 15 minutes. They report on weather and emergencies such as oil spills and floods.
This comprehensive program gives and extremely accurate picture of the health of the planet and its resources. It is said that we are consuming the natural resources of the planet at such a rate that we need one and a half planets to sustain ourselves.
The European Space Agency are providing the tools to confirm this and it is probably why the nations of Europe lead the way in energy conservation and environmental conservation..
The European Space Agency are providing the tools to confirm this and it is probably why the nations of Europe lead the way in energy conservation and environmental conservation..
The information and pictures are taken from the European Space agency web site.
|
|
This is an interesting video of the Russian launch station in Kazakhstan.
|