Sea Level Rise
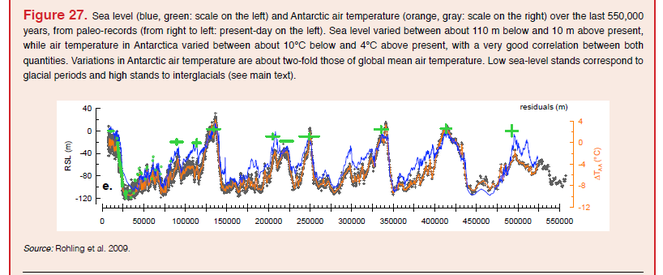
Sea level has changed considerably throughout history, from being 110 meters lower in an ice age to seven meters higher in the last warm period. Most of this is caused by the amount of water that is locked up in ice and a smaller amount by thermal expansion of the oceans.
This illustration from the World Bank report ‘Turn down the heat’
This illustration from the World Bank report ‘Turn down the heat’
To deal with thermal expansion first.
Water has a thermal expansion coefficient of 0.000214 which does not sound much, but the sea is three kilometers deep and so a one degree rise in temperature will raise the sea level 0.6 of a meter. Which is about what was originally forecast by the IPCC by 2100. The IPCC only included thermal expansion in that report as there was not enough data and research to include glacier melt.
The big numbers are in ice melt of glaciers that are on the land.
When the North Pole floating ice melts it does not affect sea level because the ice is already in the water. It might have catastrophic effects elsewhere but not to sea level.
Melting 100 gigatons of ice would raise the sea level 0.23 mm. A gigaton of ice is one kilometer high by one kilometer wide and so we need a strip 100 kilometres long.
There is a lot of ice available with Greenland alone having enough to raise sea levels 7 meters and Antarctica enough for 60 meters.
Most of human habitation is near the sea and eleven of the World's fifteen largest cities are within one meter of sea level. One meter sea level rise would be catastrophic to many nations economy.
Water has a thermal expansion coefficient of 0.000214 which does not sound much, but the sea is three kilometers deep and so a one degree rise in temperature will raise the sea level 0.6 of a meter. Which is about what was originally forecast by the IPCC by 2100. The IPCC only included thermal expansion in that report as there was not enough data and research to include glacier melt.
The big numbers are in ice melt of glaciers that are on the land.
When the North Pole floating ice melts it does not affect sea level because the ice is already in the water. It might have catastrophic effects elsewhere but not to sea level.
Melting 100 gigatons of ice would raise the sea level 0.23 mm. A gigaton of ice is one kilometer high by one kilometer wide and so we need a strip 100 kilometres long.
There is a lot of ice available with Greenland alone having enough to raise sea levels 7 meters and Antarctica enough for 60 meters.
Most of human habitation is near the sea and eleven of the World's fifteen largest cities are within one meter of sea level. One meter sea level rise would be catastrophic to many nations economy.
Greenland.
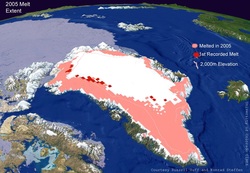
Greenland is at a lower lattitude than Antarctica and has started to melt first. It is also closer to populations and easier to research.
The glaciers nearest the sea are melting first and as they melt they no longer support the ice behind them and it starts to flow like custard on a plum pudding.
The glaciers nearest the sea are melting first and as they melt they no longer support the ice behind them and it starts to flow like custard on a plum pudding.
Reflectivity of ice,
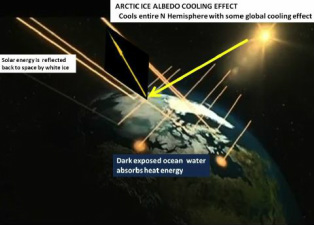
Ice in the Polar regions is important as fresh snow reflects 87% on all the heat from the Sun.
If it melts and refreezes it reflects only about 40% of the heat.
If it melts and becomes water it absorbs 90%of the Suns heat.
Due to Greenlands close proximity to Canada and the USA, soot from burning forests and from overflying aircraft settle on the ice and the dark colour causes it to absorb heat.
This is a process that is happening on Greenland and is a worrying trend.
If it melts and refreezes it reflects only about 40% of the heat.
If it melts and becomes water it absorbs 90%of the Suns heat.
Due to Greenlands close proximity to Canada and the USA, soot from burning forests and from overflying aircraft settle on the ice and the dark colour causes it to absorb heat.
This is a process that is happening on Greenland and is a worrying trend.
Transferring heat to Greenland's core.

As the ice melts and forms pools the water warms quickly. This water melts the ice in the bottom of the pool and eventually the water plunges down a hole into the interior of the glacier, which can be three kilometres thick.
This warm water makes its way to the base of the ice, which had been stuck fast to the bedrock, and releases it so that the whole glacier can slip towards the sea. It is still moving slowly but it has speeded up. If the ice does not exit to the sea it remains, warming the ice inside the glacier and steadily rotting it, making a quick collapse possible.
This warm water makes its way to the base of the ice, which had been stuck fast to the bedrock, and releases it so that the whole glacier can slip towards the sea. It is still moving slowly but it has speeded up. If the ice does not exit to the sea it remains, warming the ice inside the glacier and steadily rotting it, making a quick collapse possible.
Antarctic ice melt.
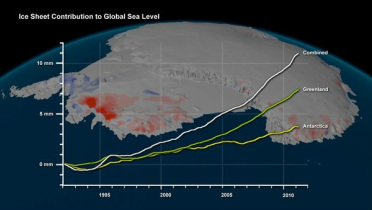
The North Pole and the Antarctic are completely different geophysical scenarios.
The North pole is sea surrounded by land and Antarctica is 3000 meter high land surrounded by ocean.
They therefore have different properties.
The North pole is sea surrounded by land and Antarctica is 3000 meter high land surrounded by ocean.
They therefore have different properties.
East and West Antarctica.
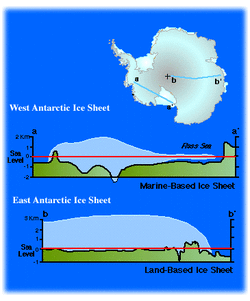
East Antarctica is based on land and is very high with ice three kilometres thick and very cold.
West Antarctica is a series of islands which anchor very thick ice in position in the sea.
Changing patterns in wind strength and sea temperature are bringing warmer water to Antarctica and this is melting sea ice from the bottom.
Several huge ice flows have broken off and disintegrated. These ice flows acted as a buffer to hold back glaciers on the land but when they disappeared the ice flow doubled its speed and started to flow into the sea.
West Antarctica is a series of islands which anchor very thick ice in position in the sea.
Changing patterns in wind strength and sea temperature are bringing warmer water to Antarctica and this is melting sea ice from the bottom.
Several huge ice flows have broken off and disintegrated. These ice flows acted as a buffer to hold back glaciers on the land but when they disappeared the ice flow doubled its speed and started to flow into the sea.
Pine Island glacier.

Pine Island is almost inaccessible but European Space Agency and NASA research satellites have observed a huge crack appearing. It is known that the ice has been melting from underneath at the rate of 50 mm a day and weakening the ice but it is worrying that the whole glacier may be coming unstable.
There is enough ice locked up in the Pine Island and adjacent Thwaites Glacier to raise sea levels five metres and if it starts to collapse it will be a dangerous threat and may result in a pulse of sea level rise .
There is enough ice locked up in the Pine Island and adjacent Thwaites Glacier to raise sea levels five metres and if it starts to collapse it will be a dangerous threat and may result in a pulse of sea level rise .
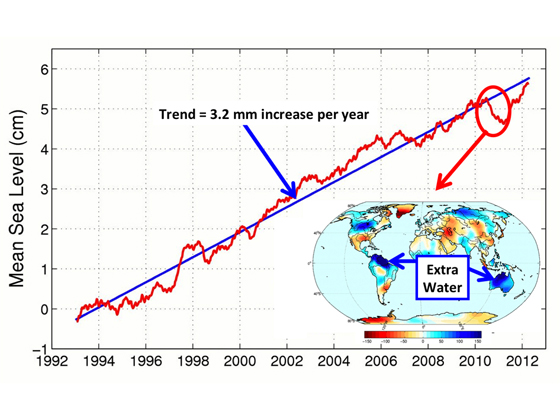
This graph shows the steady rise in sea levels and, interestingly, also shows the way sea level took a dip when water from the floods in Australia and Brazil locked up water for a few months.
One meter is critical.
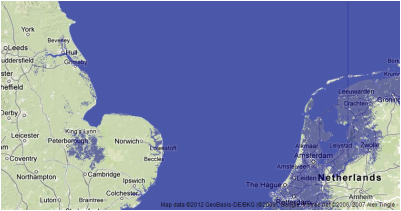
Despite the big figures mentioned in sea level rise from melting ice, the reality is that one meter would be catastrophic to the world economy, Many of our cities are located at one meter above sea level and as you can see from the map opposite a great deal of farmland is at sea level.
Many of our wells for drinking water are at sea level and these would be flooded and contaminated.
http://flood.firetree.net/
Many of our wells for drinking water are at sea level and these would be flooded and contaminated.
http://flood.firetree.net/
What is not known is how long it will take. Up until recently most of the melting has been of ice already in the sea but this is changing quickly and ice melt now matches thermal expansion in contribution to sea levels.
NASA report that sea level are rising at 3.16mm a year and this is increasing..
NASA report that sea level are rising at 3.16mm a year and this is increasing..
What does 400 ppm of CO2 mean to sea level?
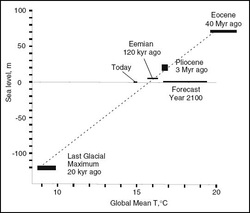
Tim Naish and other New Zealand scientists have been doing research on the Antarctic ice flow with the Andrill project. In this the team erected a drill rig on the ice and drilled through the ice floe, down through the sea and then deep into the sea bed to extract core samples for analysis.
After careful research they reached the conclusion that the last time the Earth had 400 PPM of CO2 was 4,000,000 years ago and the temperature was 3c warmer and the sea level was 12 meters higher.
After careful research they reached the conclusion that the last time the Earth had 400 PPM of CO2 was 4,000,000 years ago and the temperature was 3c warmer and the sea level was 12 meters higher.
Sea level rise can be devastating.
Losing a bit of a city is pretty bad but losing a whole country? Click the button.